BR-060 (Brazil highway)
| BR-060 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 BR-060 in Goiânia, going to Anápolis. | |
| Route information | |
| Length | 1,329.3 km (826.0 mi) |
| Major junctions | |
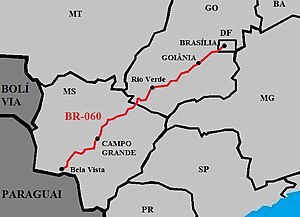
| North end | Brasília, Distrito Federal |
| South end | Bela Vista, Mato Grosso do Sul |
| Location | |
| Country | Brazil |
| Highway system | |
BR-060 is a federal highway of Brazil.[1] The 1329 kilometre road connects Brasília to Bela Vista, on the Paraguayan border.[2][3]
It is also designated as part of the Belém–Brasília Highway, in its stretch between Brasília and Anápolis.
Duplication
[edit]In the Federal District and in the State of Goiás, the highway has 521 km duplicated, between Brasilia and Jataí. The section between Brasília and Goiânia fully doubled in 2007. The section between Goiânia and Jataí doubled in 2012.[4][5]
Economic Importance
[edit]
The highway helps in the flow of agricultural production in the Center-West Region, which specializes in: soybeans, corn, sugarcane, tomatoes, beans, in the planting of eucalyptus for the production of cellulose and paper, and in cattle raising. Goiás and Mato Grosso do Sul also have considerable mineral exploration, producing a lot of iron ore, nickel and copper, in addition to gold, manganese and niobium. The BR-060 will in the future serve as a link with the Bioceanic Corridor that is being built with 3 other South American countries, connecting Campo Grande to Antofagasta, passing through Paraguay, northern Argentina and northern Chile. [6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13]
The highway is also of tourist importance, as it connects to Pantanal, the largest wetland in the world, and Bonito, an important Brazilian tourist city. [14][15][16][17][18]
References
[edit]- ^ "BR-60". Ministry of Transport. Archived from the original on 22 November 2012. Retrieved 7 June 2011.
- ^ BR 060 map
- ^ Rodovias Radiais
- ^ Trechos duplicados da BR-060/GO serão liberados ao tráfego em março
- ^ "BR-060, entre Brasília e Goiânia, é filé mignon de leilão". Archived from the original on 2019-05-31. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
- ^ Cronograma da Rota Bioceânica segue com obras em ritmo acelerado no Paraguai
- ^ "Encontro do Corredor Bioceânico avança em projetos turísticos, culturais e comerciais". Archived from the original on 2020-02-23. Retrieved 2021-03-13.
- ^ IBGE prevê safra recorde de grãos em 2020
- ^ MS deve registrar maior safra de soja da história e produção pode chegar a mais de 11 milhões de toneladas
- ^ Goiás é o segundo maior produtor de cana-de-açúcar do País
- ^ Com quarto maior rebanho bovino do país, MS recebe evento para debater todos os elos da cadeia produtiva
- ^ MS se consolida como maior exportador de celulose do país
- ^ Anuário Mineral Brasileiro 2018
- ^ McClain, Michael E. (2002). The Ecohydrology of South American Rivers and Wetlands. International Association of Hydrological Sciences. ISBN 1-901502-02-3. Retrieved 2008-08-31.
- ^ Susan Mcgrath, photos by Joel Sartore, Brazil's Wild Wet, National Geographic Magazine, August 2005
- ^ Keddy, Paul; Fraser, Lauchlan (2005). The World's Largest Wetlands: Ecology and Conservation. Cambridge University Press. Retrieved 2008-08-31.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Rhett A. Butler. "Pantanal, the world's largest wetland, disappearing finds new report". mongabay.com. Retrieved 2006-01-10.
- ^ "The World's largest wetland". The Nature Conservancy. Archived from the original on 2008-01-23. Retrieved 2008-01-21.

